20k bladder tear test|bladder pressure testing procedure : private label If the health care provider suspects an injury, you may have the following tests: Retrograde urethrogram (an x-ray of the urethra using dye) for injury of urethra; Retrograde cystogram .
Biohazardous waste must be autoclaved prior to its disposal. Two autoclaves (machines #1 and #2) in room 2427 VMBSB are reserved for this process (‘Biokill’). The machines are operated .
{plog:ftitle_list}
TERRA Food-Tech ® autoclaves can sterilize and pasteurize food packaged in cans, glass or plastic. They are designed for the cooking, sterilization and pasteurization of packaged foods using a heart temperature probe placed on .
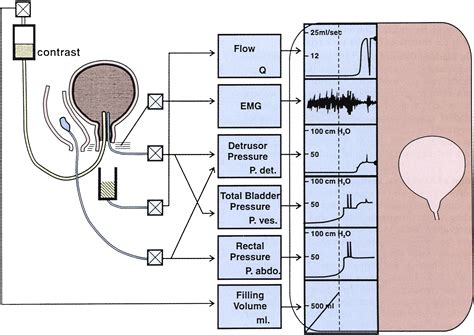
Each type of urodynamic test works a little differently. Your healthcare provider may even perform multiple tests at one time to get the best understanding of how . See moreMost of the tests don’t require any special planning. For some, your provider may ask you to drink fluids before the test so that your bladder is full. Be sure to ask . See moreUrodynamic testing is extremely safe and reliable. There’s a small chance of developing a urinary tract infection due to inserting a catheter into your urethra. See more
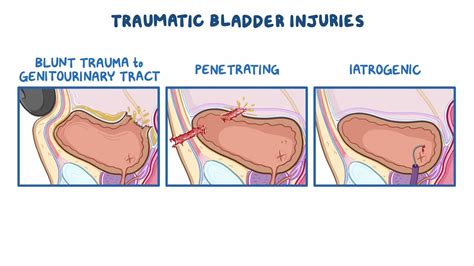
Urodynamic tests shouldn’t be painful. You may feel soreness for up to 24 hours afterward, but you shouldn’t have severe pain. See more The clinical features, diagnosis, and management of traumatic and iatrogenic bladder injuries are reviewed here. (See "Overview of traumatic lower genitourinary tract .If the health care provider suspects an injury, you may have the following tests: Retrograde urethrogram (an x-ray of the urethra using dye) for injury of urethra; Retrograde cystogram . Bladder trauma is an uncommon injury that can be caused by a direct blow to a distended bladder, high energy injury which disrupts the pelvis, penetrating, and iatrogenic injuries. Bladder traumas are divided into broad .
Ureteral injuries should be suspected in complex, multisystem abdominopelvic trauma patients, such as those with bowel, bladder, or vascular injuries; in those with complex pelvic/vertebral .
watertight closure bladder trauma
Diagnosis: Bladder rupture can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as: Abdominal ultrasound. Computed .Despite its frequency, there is limited research on best practices for bladder injury repair. This literature review aims to summarize types of iatrogenic bladder injuries, guidelines on bladder . The present study seeks to summarize contemporary management of bladder trauma at our tertiary care center, assess the impact of length of catheterization on bladder . Bladder injury is milder, manifesting as bruises or tears without urine leakage, while bladder rupture involves a complete tear leading to urine escape. Types of bladder .
Laboratory Studies. In the subacute setting, the serum creatinine level can aid in the diagnosis of bladder rupture. In the absence of acute kidney injury and urinary tract .
urodynamic bladder test results
Urodynamic tests help diagnose issues with your bladder, urinary sphincter (the muscle between your bladder and urethra) and urethra, which are also known as your lower urinary tract. The tests measure how well you store and release pee (urine). The clinical features, diagnosis, and management of traumatic and iatrogenic bladder injuries are reviewed here. (See "Overview of traumatic lower genitourinary tract injury" and "Traumatic injury to the male anterior urethra, scrotum, and penis" and "Posterior urethral injuries and management".)
If the health care provider suspects an injury, you may have the following tests: Retrograde urethrogram (an x-ray of the urethra using dye) for injury of urethra; Retrograde cystogram (imaging of bladder) for injury of the bladder; CT scan; The exam may also show: Bladder injury or swollen (distended) bladder
Bladder trauma is an uncommon injury that can be caused by a direct blow to a distended bladder, high energy injury which disrupts the pelvis, penetrating, and iatrogenic injuries. Bladder traumas are divided into broad categories of extraperitoneal (EP), intraperitoneal (IP), or combined injuries which guide the management plan.Ureteral injuries should be suspected in complex, multisystem abdominopelvic trauma patients, such as those with bowel, bladder, or vascular injuries; in those with complex pelvic/vertebral fractures; after rapid deceleration injuries; and when the trajectory of the penetrating injury is near the ureter, especially with high velocity gunshot .
Diagnosis: Bladder rupture can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as: Abdominal ultrasound. Computed tomography (CT) scan. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Cystogram (X-ray of the bladder) Treatment: Treatment for bladder rupture depends on the severity of the injury.Despite its frequency, there is limited research on best practices for bladder injury repair. This literature review aims to summarize types of iatrogenic bladder injuries, guidelines on bladder injury repair, expected follow-up care, and areas for further research. The present study seeks to summarize contemporary management of bladder trauma at our tertiary care center, assess the impact of length of catheterization on bladder injuries and complications, and develop a protocol for management of bladder injuries from time of injury to catheter removal.
does urban body jewelry come autoclaved
Bladder injury is milder, manifesting as bruises or tears without urine leakage, while bladder rupture involves a complete tear leading to urine escape. Types of bladder rupture include intraperitoneal and extraperitoneal rupture. Laboratory Studies. In the subacute setting, the serum creatinine level can aid in the diagnosis of bladder rupture. In the absence of acute kidney injury and urinary tract obstruction,.
Urodynamic tests help diagnose issues with your bladder, urinary sphincter (the muscle between your bladder and urethra) and urethra, which are also known as your lower urinary tract. The tests measure how well you store and release pee (urine). The clinical features, diagnosis, and management of traumatic and iatrogenic bladder injuries are reviewed here. (See "Overview of traumatic lower genitourinary tract injury" and "Traumatic injury to the male anterior urethra, scrotum, and penis" and "Posterior urethral injuries and management".)If the health care provider suspects an injury, you may have the following tests: Retrograde urethrogram (an x-ray of the urethra using dye) for injury of urethra; Retrograde cystogram (imaging of bladder) for injury of the bladder; CT scan; The exam may also show: Bladder injury or swollen (distended) bladder
Bladder trauma is an uncommon injury that can be caused by a direct blow to a distended bladder, high energy injury which disrupts the pelvis, penetrating, and iatrogenic injuries. Bladder traumas are divided into broad categories of extraperitoneal (EP), intraperitoneal (IP), or combined injuries which guide the management plan.Ureteral injuries should be suspected in complex, multisystem abdominopelvic trauma patients, such as those with bowel, bladder, or vascular injuries; in those with complex pelvic/vertebral fractures; after rapid deceleration injuries; and when the trajectory of the penetrating injury is near the ureter, especially with high velocity gunshot . Diagnosis: Bladder rupture can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as: Abdominal ultrasound. Computed tomography (CT) scan. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Cystogram (X-ray of the bladder) Treatment: Treatment for bladder rupture depends on the severity of the injury.Despite its frequency, there is limited research on best practices for bladder injury repair. This literature review aims to summarize types of iatrogenic bladder injuries, guidelines on bladder injury repair, expected follow-up care, and areas for further research.
dolby medical autoclaves
The present study seeks to summarize contemporary management of bladder trauma at our tertiary care center, assess the impact of length of catheterization on bladder injuries and complications, and develop a protocol for management of bladder injuries from time of injury to catheter removal. Bladder injury is milder, manifesting as bruises or tears without urine leakage, while bladder rupture involves a complete tear leading to urine escape. Types of bladder rupture include intraperitoneal and extraperitoneal rupture.
urethra injury test results
Invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, autoclaves use high pressure and steam to destroy microorganisms by denaturing their proteins, rendering them harmless. This makes autoclaves invaluable for ensuring that .The dental autoclave is an essential element in dentistry as it is used to sanitize handpieces and other dental instruments after use. The dental autoclave uses high-pressure temperature and steam to eliminate bacteria and remove debris from handpieces. This dental equipment is designed and . See more
20k bladder tear test|bladder pressure testing procedure